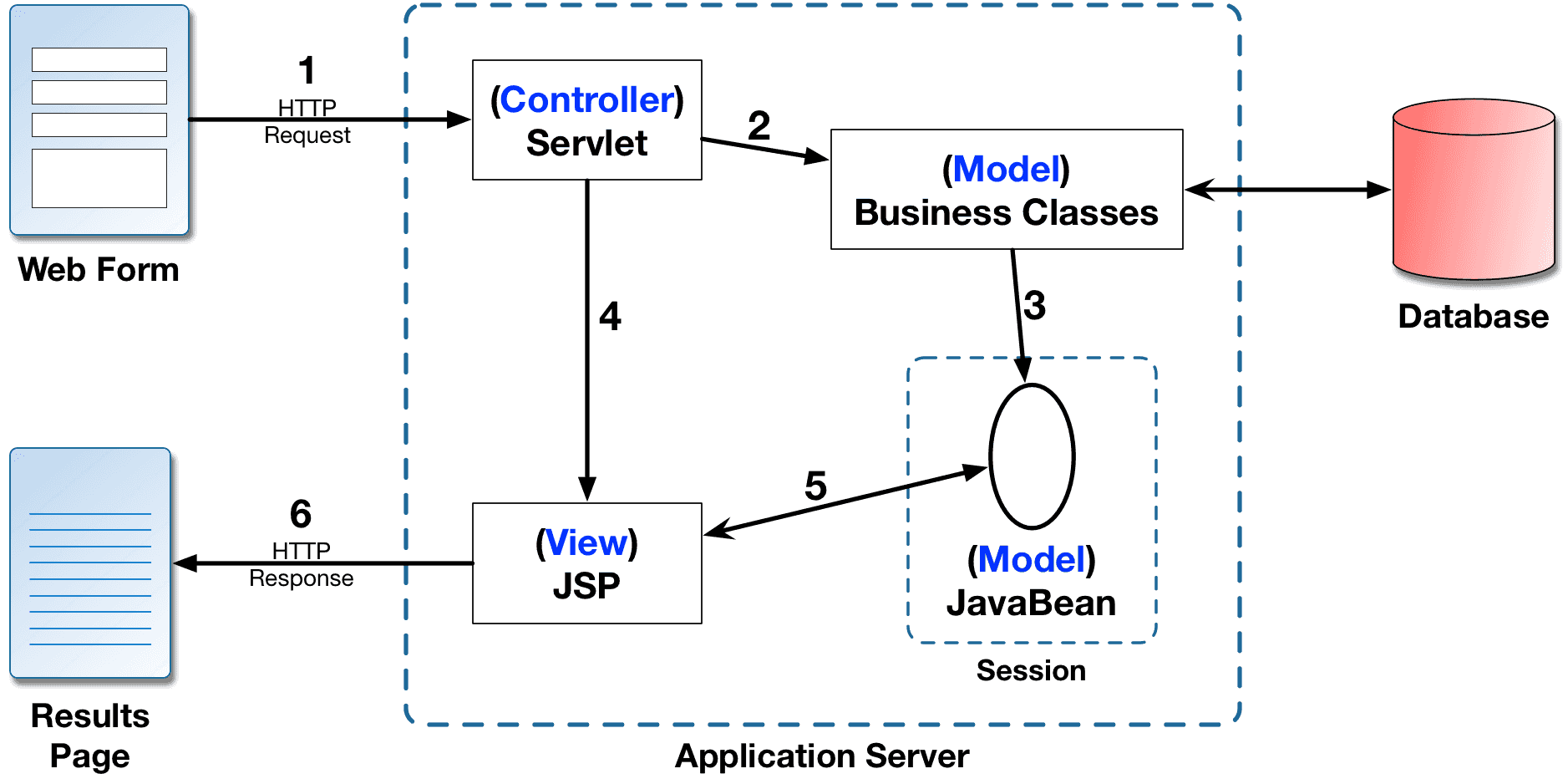
Model View Controller - MVC
Integrating Servlets and JSP
Concepts
- Understanding the benefits of MVC
- Using RequestDispatcher to implement MVC
- Forwarding requests from servlet to JSP pages
Understanding the Need for MVC
Simple application or * Call Java code directly.
small development team. * Call Java code indirectly.
| * Use JavaBeans.
| * Use the MVC architecture.
| * Use the JSP expression language.
v * Use JSP 2.0 and JSTL.
Complex application or * Use Custom tags.
large development team. * Use a web development framework.
- Servlets are great for handling HTTP Requests and for general Java coding.
- Business logic really belongs in Java classes that don’t know anything about HTTP.
- JSP is really good at presentation of information.
- The best approach is to use all three! We let each part do what it is best at.
- The formal name for this approach is the Model View Controller (MVC) architecture.
MVC Overview in Web Applications
Implementing MVC
- Define JavaBeans to represent the data.
- Use a servlet to handle HTTP Requests.
- Populate the JavaBeans using business classes.
- Store the JavaBeans in the request, session, or servlet context.
- Forward or Redirect the request to a JSP page.
- Extract the data from the JavaBeans on the JSP pages.
JavaBeans? What are JavaBeans?
- JavaBeans are just plain, old, Java classes (POJOs) that follow a few rules.
- A JavaBean must have a zero-argument constructor.
- A JavaBean should have only private instance variables.
-
A JavaBean should have proper get and set methods for its instance variables.
-
For non-boolean variables you should have get and set methods:
private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } -
For boolean variables you should have a set method and an “is” method:
private boolean connected; public boolean isConnected() { return connected; } public void setConnected(boolean connected) { this.connected = connected; }
-
-
Example: BeanOne.java
Using JavaBeans in JSP
- When using JavaBeans on a JSP page we’ll use the EL.
-
A servlet could create a bean and put it in the session.
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { BeanOne bean = new BeanOne(); request.setAttribute("myCoolBean", bean); String url = "/beanOneDemo.jsp"; RequestDispatcher dispatcher = getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher(url); dispatcher.forward(request, response); } -
Then we access the data property like this example:
- ${myCoolBean.data}